CA 125 (Ovarian Cancer Marker)
In the space of cancer diagnostics, tests like CA 125 play a crucial role, particularly in the detection and management of ovarian cancer. CA 125 is a biomarker that holds significance in diagnosing and monitoring certain ovarian cancer. In this blog we dive into what CA 125 is and how it functions as a vital tool in healthcare.
The Importance of CA 125 test
While the CA 125 test is commonly associated with the detection and monitoring of ovarian cancer, its versatility extends beyond this single application. Understanding the various health conditions that can be detected through a CA 125 test is essential f
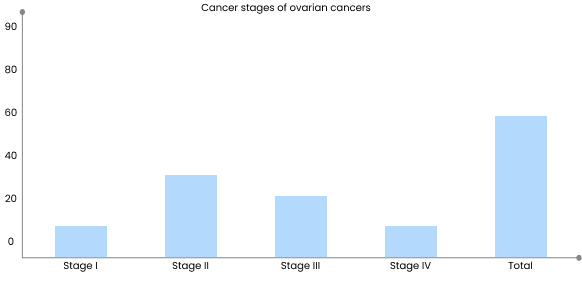
Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian cancer is perhaps the most well-known condition detected through the CA 125 test. Elevated levels of CA 125 in the blood can often indicate the presence of ovarian cancer. However, it's important to note that not all women with ovarian cancer will have elevated CA 125 levels, particularly in the early stages of the disease.
Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a common gynecological condition characterised by the growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, pain, and sometimes infertility. Women with endometriosis may have elevated CA 125 levels, especially during periods of active inflammation or when endometrial tissue is actively growing or shedding.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted bacteria. In cases of severe or chronic PID, CA 125 levels may be elevated due to inflammation and tissue damage within the pelvic region.
Non-Cancerous Ovarian Cysts: Non-cancerous ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, some may cause symptoms or complications. Elevated CA 125 levels may be observed in women with certain types of ovarian cysts, particularly those associated with inflammation or hemorrhage.
Peritoneal Inflammation: The peritoneum is the membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering the abdominal organs. Inflammatory conditions affecting the peritoneum, such as peritonitis or peritoneal tuberculosis, can lead to elevated CA 125 levels due to increased production and release of the CA 125 protein from inflamed tissues.
Other Gynecological Cancers: In addition to ovarian cancer, certain other gynecological cancers, such as endometrial cancer and fallopian tube cancer, may cause elevated CA 125 levels. These cancers may involve the same tissues or structures that produce CA 125, leading to its release into the bloodstream.
Who Needs To Take The CA 125 Test?
High-risk individuals, such as those with a family history of ovarian cancer or known genetic mutations, stand to benefit from regular CA 125 testing as part of a proactive screening regimen. Similarly, women presenting with symptoms suggestive of ovarian cancer, such as abdominal discomfort or changes in bowel habits, may undergo the CA 125 test to aid in diagnosis. Additionally, individuals with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer, especially those with known BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, may be advised to undergo testing. Women with a personal history of breast, colon, or endometrial cancer may also be at higher risk and may benefit from ovarian cancer testing. Further, women with abnormal pelvic imaging findings or certain postmenopausal individuals may undergo CA 125 testing as part of their routine healthcare management. For those already diagnosed with ovarian cancer, the CA 125 test serves as a crucial monitoring tool, helping healthcare providers assess treatment effectiveness and detect disease recurrence. While routine screening for ovarian cancer in the general population is not recommended due to test limitations, targeted use of the CA 125 test in high-risk groups or those with concerning symptoms can impact detection & treatment outcomes.
The Testing Process
Evaluating The Results
| Age Group | CA-125 Levels* |
|---|---|
| 17-25 Years (n=18) | 109.55 ± 109.48 |
| 25-35 Years (n=28) | 104.40 ± 92.86 |
| 35-47 Years (n=14) | 170.96 ± 264.94 |
| All Subjects (n=60) | 119.61 ± 147.95 |
*Expressed as mean and standard deviation.
What Does The Normal CA 125 Range Mean?
The normal range for CA-125 levels typically falls below 35 units per milliliter (U/mL) in most laboratories. However, it's important to note that this reference range can vary slightly between different laboratories and may be influenced by factors such as age, menstrual cycle, and individual health conditions. Additionally, CA-125 levels can fluctuate in response to various factors, so interpretation of test results should always be done in consultation with a healthcare provider who can consider the individual's medical history and clinical context. Elevated CA-125 levels may indicate the presence of certain medical conditions, including ovarian cancer, but further evaluation is necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
What Does A High CA 125 Level Indicate?
Risk Associated With The Test
False Positives: A false positive occurs when the CA 125 test indicates elevated levels of the protein in the absence of ovarian cancer. Several non-cancerous conditions, such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and non-cancerous ovarian cysts, can also cause CA 125 levels to rise. This can lead to unnecessary anxiety and further invasive diagnostic procedures.
False Negatives: Conversely, a false negative occurs when the CA 125 test indicates normal levels of the protein despite the presence of ovarian cancer. Not all women with ovarian cancer will have elevated CA 125 levels, especially in the early stages of the disease. Therefore, a normal CA 125 result does not rule out the possibility of ovarian cancer.
Over Diagnosis and Overtreatment: Routine screening for ovarian cancer using the CA 125 test is not recommended for the general population due to the risk of over diagnosis and overtreatment. Ovarian cancer is relatively rare, and the test may lead to unnecessary surgeries or treatments for benign conditions.
Psychological Impact: A positive CA 125 test result or the need for further diagnostic procedures can cause significant psychological distress and anxiety for individuals, even if the final diagnosis is benign. Adequate support and counseling may be necessary to address these emotional concerns.
Costs and Resources: Diagnostic tests, including the CA 125 test, can incur financial costs for individuals and healthcare systems. Additionally, further diagnostic procedures and treatments for suspected ovarian cancer can require significant resources and may not always be covered by insurance.
Invasive Procedures: In some cases, a positive CA 125 test result may lead to further invasive diagnostic procedures, such as imaging scans, biopsies, or exploratory surgery, to confirm or rule out ovarian cancer. These procedures carry their own risks, including bleeding, infection, and complications from anesthesia.
Lifestyle Tips To Maintain Ovarian Health
Balanced Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients and antioxidants that support overall health, including ovarian health. Limiting processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats is also beneficial.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity promotes circulation, helps maintain a healthy weight, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases, including certain cancers. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health authorities.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and excess body fat can disrupt hormone balance and increase the risk of ovarian and other reproductive cancers. Strive to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of balanced diet and regular exercise.
Avoid Tobacco: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer and other reproductive health issues. If you smoke, consider quitting, and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke whenever possible.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake has been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels, defined as up to one drink per day for women.
Practice Safe Sex: Practicing safe sex and using protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can help reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can affect ovarian health.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone levels and overall health. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies that you enjoy into your daily routine.
Regular Health Check-ups: Attend regular gynecological check-ups and screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider. Discuss any concerns or symptoms related to ovarian health during these appointments.
Hormonal Balance: Pay attention to hormonal balance and seek medical advice if you experience irregular menstrual cycles, hormonal imbalances, or symptoms such as pelvic pain or abnormal bleeding.
Fertility Awareness: If you plan to conceive in the future, consider fertility awareness methods to understand your menstrual cycle and ovulation patterns. This can help optimise fertility and overall reproductive health.
Conclusion
The CA 125 test serves as a valuable tool in the detection and monitoring of ovarian cancer, although its application extends beyond this singular purpose. While elevated CA 125 levels are commonly associated with ovarian cancer, it's essential to recognise that various factors can influence test results, leading to both false positives and false negatives. Interpretation of CA 125 test results should be done in conjunction with other clinical findings, individual risk factors, and medical history. Additionally, routine screening for ovarian cancer in the general population is not recommended due to the risk of over diagnosis and overtreatment. Instead, targeted use of the CA 125 test is recommended for high-risk individuals, those with concerning symptoms, and individuals undergoing treatment or surveillance for ovarian cancer. Ultimately, shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers is crucial to ensure informed choices regarding ovarian cancer screening, diagnosis, and management, taking into account the potential benefits, limitations, and risks associated with the CA 125 test. on www.flebo.in . Regular communication, proactive lifestyle choices, and adherence to recommended screening guidelines can contribute to better ovarian health.