Blood Group Testing: Procedure, Precautions & How To Check Blood Group
Blood Group Test: An Overview
Blood is a specialized body fluid with four core components- the plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Although the blood across the species consists of the same factor, it varies from person to person due to different genetics- the unique combination of protein molecules that are subdivided into antigens and antibodies.
The need for blood group test and identifying blood groups were discovered in 1901 by Karl Landsteiner, an Austrian scientist destroying the belief that all blood was the same, which was causing deaths from blood transfusions.
There are eight kinds of blood types and four major blood groups based on blood containing two specific antigens- A and B. This system of performing a blood group test to identify the blood type is called the ABO Blood Group System.

Types of Blood Groups
According to the ABO Blood Group System, there are 8 blood types, with 4 major blood groups based on the presence of the antigens- A or B.
The 8 blood types are:
1. A positive (A+): One of the most common blood types. A person with this blood type can give blood to people who are of blood type A+ or AB+.
2. A negative (A-): An individual with A- blood type can only donate blood to A and AB blood groups, regardless of the positive and negative.
3. B positive (B+): B+ blood can be donated to a person with B+ or AB+ blood type.
4. B negative (B-): B- blood can be transfused to an individual with B or AB blood type.
5. AB positive (AB+): People with AB+ blood type are called universal recipients, and can receive any blood type.
6. AB negative (AB-): A person with AB- blood type can donate blood to a person of any blood group. They are called universal plasma donors.
7. O positive (O+): A person with O+ blood can donate blood to an individual with any positive blood type.
8.O negative (O-): This blood type can be received by people of any blood type, regardless of positive or negative.
Major Blood Groups
The four major blood groups, based on the presence of A and B antigens are:
- Group A, has the A type antigen and B type antibody
- Group B, has B antigen and A antibody
- Group AB, has both A and B antigens but no antibodies
- Group O does not have either of the antigens but has both A and B antibodies.
There is another antigen called the Rh Factor, and its presence or absence determines the blood compatibility between two individuals.
Why do we need to know blood types?
Knowledge of blood types is important to avoid transfusing a foreign blood type into an individual’s body.
Mixing the blood of two people with different blood types can cause clumping of the blood, which is fatal, and life-threatening. This is so because the person receiving the unmatching blood type has antibodies that will fight the cells of the donated blood, resulting in a toxic reaction.
Therefore, for a safe, non-threatening blood transfusion, the donor and the receiver have to have compatible blood types that can be mixed without causing a fatal reaction.
Blood Group Testing
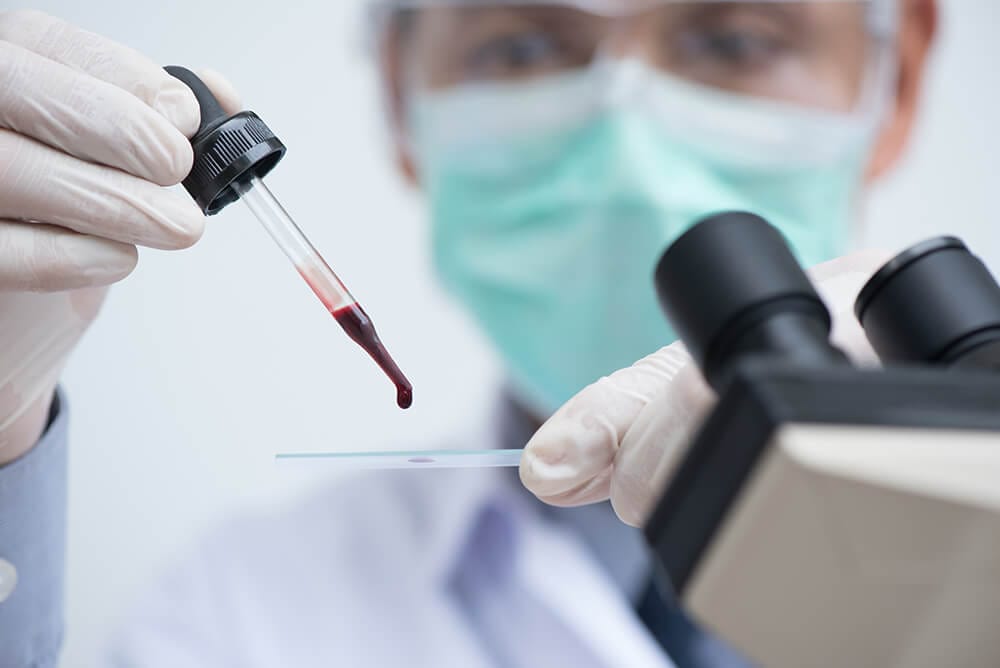
Blood group testing to determine a blood type is called ABO Typing or Forward Typing. The test is typically performed by a phlebotomist or a medical professional. In this test, a blood sample is mixed with antibodies against type A and type B blood. The sample is then checked for clumps (agglutination), ie. whether or not the blood cells stick together.
The sticking, clumping of blood cells indicates the reaction of blood cells with the antibodies.
For example, mixing a blood sample with antibodies against type A blood (anti A antibodies) shows that the blood sample is of blood group A.
The next step to determine the blood type is called Reverse or Back Typing. In this test, the liquid part, minus the cells, of the blood sample is mixed with both blood types A and B.
It is a known fact that Type A blood has anti-B antibodies, and vice versa. However, Type O blood contains both antibodies. So if the agglutination occurs when the liquid is mixed with type A blood, it will mean that the final blood type of the sample is B.
For Rh Factor testing, the blood sample will simply be mixed with an anti-Rh serum. If the blood cells clump together, it means that the sample is Rh-positive.
Blood Group Testing Methods
There are different ways to determine a blood group of an individual. One way is to visit the doctor and have a phlebotomist take the blood sample and send it to the laboratory to get tested. Other options for blood group testing include blood tests at home, free blood group testing, and blood grouping procedure without drawing blood.
Let’s throw some light on these lesser-known options:
- Blood Grouping Test at home: To perform a blood grouping test procedure at home, you have to first purchase a blood typing kit. The test involves pricking the patient’s finger with a lancet (which comes with the kit) and putting the drops of blood on a special blood grouping test card.
After that, you simply have to observe the card for blood clumps and spreading out, and match the reactions with an included guide.
Some home blood grouping tests also come with vials of fluid in place of a card, you can check as per your preference before buying the test.
- Finding the blood group for free: Another way to find your blood type is to donate blood. You can simply ask the staff to tell you the blood type after donating your blood. Although you might have to wait for a couple of weeks for the results since donated blood is not tested right away.
- Blood grouping test without sampling blood: For people who are scared of needles, or don’t want to get their blood drawn can also get their blood group tested through saliva or other body fluids.
80% of the people secrete blood group antigens in their saliva, urine, mucus, and sweat, and are called the Secretors. The kit first determines whether the individual is a secretor, to determine the ABO blood type.

Risks from Blood Group Testing
Blood type testing is usually a safe procedure for most, however, they do have some risks if the procedure is not executed with utmost care. Discomfort and pain while inserting the needle to draw blood, excessive bleeding, bruising, or infection post-procedure, on the sample site is also pretty common due to carelessness.
Conclusion
Blood tests are important to keep your physical well-being in check. Getting tested regularly helps you see what changes your body is going through, with age and guides you to make sound decisions accordingly.
FAQ
Are blood group tests accurate?
Blood grouping tests are accurate 99.99% of the time. The accuracy issue may arise while testing the rarest blood types.
Why is the blood red?
The blood turns red due to the presence of Hemoglobin, which is picked up when the blood gets oxygenated in the lungs. As the blood travels through the body, the hemoglobin releases oxygen to the parts.
What are the three main components of blood?
Red Blood Cells (they carry oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body)
White Blood Cells (they aid the immunity system and fight infections)
Platelets (they help in blood clotting during injuries).