Phlebotomy & Phlebotomists
What is Phlebotomy?
The process of drawing blood from a vein in the arm is called Phlebotomy. Also known as a blood draw or venipuncture this is an important primary step in diagnosing medical conditions.
Phlebotomy is usually done to send the drawn blood to the laboratory, to analyze the condition and find the right treatment for the disease, however, there are times the venipuncture is carried out to reduce the overflow of blood inside the body.
There are certain medical situations where blood needs to be withdrawn as a part of treatment. This is called Therapeutic Phlebotomy. People suffering from Hemochromatosis (excess of iron in the body), Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), or Polycythemia Vera (blood cancer in the bone marrow) are some of the major conditions where Therapeutic Phlebotomy is considered as one of the essential treatments.
Who is a Phlebotomist?
Phlebotomy is a complex procedure that requires expert knowledge of the blood, and the veins of the body. One wrong puncture can cause serious injuries, and sometimes death.
A Phlebotomist is a medical worker who carries out the procedure of Phlebotomy. He collects blood from patients and prepares samples for testing and diagnosis. The professional also is in charge of taking blood pressure, pulse and respiration readings of patients.
A phlebotomist is a very significant member of the health care team since a part of their job is to decipher among the blood test samples and have deep knowledge of how various medications and diets can impact the blood of the patient.
Some of the additional tasks of a phlebotomist are to explain the procedure of phlebotomy to the patient and his family to put their minds at ease, and to comfort a patient who is nervous before the phlebotomy or has a fear of needles.
Qualifications of a Phlebotomist
The process of phlebotomy consists of intricate work and attention to detail. The inserting of needles into the hidden, hard to locate veins of conscious patients is a difficult task and requires a professional with fine motor skills, the necessary diplomas and degrees in the field, and knowledge of the human body.
To become a phlebotomy professional, a high school degree and a diploma certificate in phlebotomy training are necessary. Several organizations provide certification in the field, like the American Society of Clinical Pathologists, and the National Healthcareer Association.
However, applicants must have their high school diplomas and the phlebotomy training certificate to apply to the above-mentioned institutions.
What are the procedures in Phlebotomy?
Like all medical procedures and operations, Phlebotomy must be performed to maintain patient safety and preserve venous integrity, to avoid any accidents or injuries.
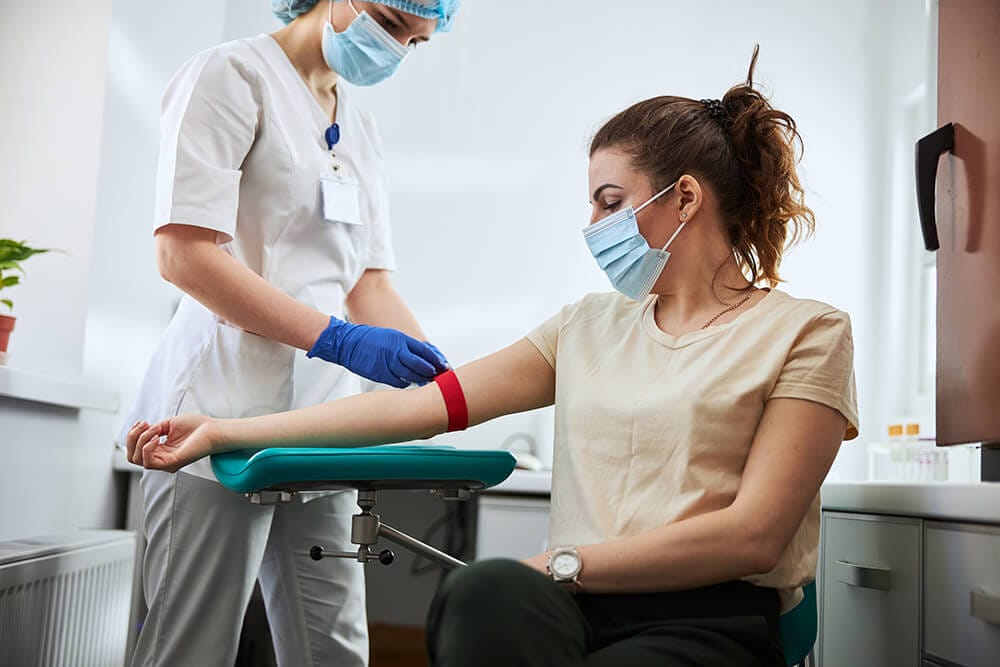
The process of Phlebotomy may or may not require the patient to fast for 8-12 hours prior, as per the doctor’s instructions. To start the procedure, the patient is always asked to sit on a comfortable chair or simply lie down. To locate the vein, and insert the needle to draw the blood, the phlebotomist will ask the patient to make a fist with the hand on which the Phlebotomy is needed to be performed.
Oftentimes, the professional ties a band, which is known as a tourniquet around the patient’s upper arm to make the vein pop out, and thus easy to locate.
The needle used to draw the blood is attached to a small tube that is filled during the phlebotomy. If you’re getting blood drawn for tests, you might need to fill more than a single test tube.
However, if you’re getting blood removed as a part of a treatment for a medical condition, the amount of blood drawn, and time taken completely depends on individual patient needs.
After the procedure, the area is cleaned and bandaged to avoid any infections and to stop the bleeding.

Methods of Phlebotomy
There are 3 most common methods to perform a phlebotomy, collect blood. There are:
-
- Arterial Sampling: In this method of phlebotomy, the blood in this procedure is drawn from the artery to determine arterial blood gases, monitor the flow of carbon dioxide in the body, and identify metabolic, respiratory, and acid-base disorders in the patient.
- Venipuncture Sampling: Venipuncture Sampling is the most commonly opted method to collect blood from patients. The needle is inserted in the superficial vein of the upper arm (also called the median cubital vein).
- Fingerstick Sampling: Blood is drawn from the tip of the finger when there is a requirement for very little blood, or the patient is nervous about needles.
History of Phlebotomy
Although today, Phlebotomy is used to cure or diagnose only a few blood diseases, the procedure has been a popular cure for treating common medical ailments like fever, headache, appetite loss, and digestion issues for generations.
The practice of drawing blood from veins and arteries was started by the Egyptians and spread to the Greeks and Romans as it gained popularity.
However, the practice of treating common diseases with phlebotomy was considered controversial and dangerous after George Washington died from excessive blood loss due to phlebotomy in 1799.
By the end of the 19th century, bloodletting was marked as an ineffective practice for the treatment of common ailments and was soon stopped.
Risks and Side Effects
Phlebotomy is usually a very safe procedure, with very low chances of side effects or any risks. However, there have been rare incidents where the patients have incurred nerve damage, vasovagal reaction, and infections post the procedure.
The Best Phlebotomy practices
For safe phlebotomy, a phlebotomist must follow these practices to avoid any patient injuries:
-
- Appropriate location: Choosing an appropriate, calm location for the phlebotomy is important for the professional. A well-lit, clean, and equipped area is needed for a successful procedure.
- Quality Check: Quality assurance regarding the equipment, and the medical workers is key for the prevention of infections, mishaps, and patient safety. The main points for quality assurance during phlebotomy are Education and training, maintenance of the standard operating procedures, and proper identification of the patient.
- Planning Beforehand: Step-wise planning of the phlebotomy before actually starting with the process is important to avoid missing any significant steps during the procedure.
- An abundance of supplies and equipment before the procedure: Procurement of supplies for hand hygiene such as gloves, sanitizer, needles, and syringes must be available before the procedure.
- Patient cooperation: A successful procedure involves patient cooperation and understanding.
Important points to remember before a Phlebotomy:
-
-
- Reputation and Certification of the lab: To determine the authenticity and professionalism of a lab, check its credentials. NABL and CAP are the most common certificates to look out for in a laboratory.
- Hygiene: Use of clean gloves, masks, and fresh syringes while performing the phlebotomy or drawing blood should be practiced to avoid infections.
- Skin Antisepsis: Cleaning of the collection area before drawing blood with antiseptic.
- Post-procedure Care: The phlebotomist must place gauze or cotton on the site after drawing blood, to stop the bleeding.
- Disposal of Waste: Destructing the syringe after the procedure, and disposal of the medical waste must be done right after the procedure to avoid re-use.
-
Conclusion
Phlebotomy is a vital part of modern medicine and is used as a treatment for many diseases. It is also the mainstay of medical science since drawing uncontaminated, fresh blood is the basis of diagnosing medical conditions to provide further treatment to patients.
FAQs
1. What is the role of Phlebotomy in healthcare?
Phlebotomy is a procedure that involves collecting blood from patients as a part of a treatment or to prepare samples for testing.
2. What are the complications caused due to venipuncture?
Hematoma, nerve damage, syncope, and fainting are some of the complications of venipuncture.
3. Time taken to recover from phlebotomy?
Patients take 24 to 48 hours to recover from this procedure. Recovery time can vary from patient to patient.
4. What hemoglobin level requires phlebotomy?
Patients with hemoglobin lower than 12.5g/dL should not appear for phlebotomy.