B12 Vitamin Foods: 12 Vitamin B12 Rich Food For Vegetarians & Non Vegetarians
Overview of b12 vitamin foods
Vitamin b12, also called cobalamin, is an essential nutrient for the formation of red blood cells. It is a water-soluble vitamin that boosts the production of brain and nerve cells. Vitamin b12 is most commonly found in animal foods. It is synthesized in the form of protein and is broken down into the stomach. The small intestine absorbs the free vitamin b12. However, food supplements contain vitamin b12 in free form that makes it easier for the body to absorb. Since this nutrient is most commonly available in animal foods, many vegetarians have vitamin b12 deficiency that leads to reduction of white and red blood cells in the body. Vitamin b12 deficiency may also cause fatigue, weight loss, anaemia, muscle weaknesses, and infertility. Hence, read below to find out the best vitamin b 12 food sources for vegetarians, non vegetarians and vegans,
Vitamin b12 deficiency causes
Vitamin b12 obtained from foods is to be broken down into free form that combines with intrinsic factors in the body for absorption. Since it isn’t easily available in free form, a lot of people suffer from vitamin b12 deficiency. The following are the most common vitamin b12 deficiency causes:
- Pernicious anemia:- It is an autoimmune disease that affects the mucus in the gastric region. This reduces the production of intrinsic factors in the body and causes poor absorption of vitamin b12 in the body. Therefore, people with pernicious anemia have vitamin b12 deficiency even if they consume sufficient vitamin b12 foods.
- Gastrointestinal disorders:- People who have gastrointestinal orders like celiac disease or bowel disease are more prone to vitamin b12 deficiency as the stomach cells that produce hydrochloric acid get damaged. Similarly, people who have undergone gastrointestinal surgery or partial removal of stomach or small intestine have low levels of vitamin b12 in the body.
- Vegetarian diet:- Another major cause of vitamin b12 is a pure vegetarian diet for the long term. Vitamin b12 is mostly found in animal foods like meat, eggs, tuna, beef liver and salmon. Therefore, vitamin b12 deficiency is more common in vegetarians and vegans. Even infants that have vegetarian mothers can have vitamin b12 deficiency as they mostly feed breast milk.
- Old age:- Age can also be a crucial factor for vitamin b12 deficiency in the body. During old age, the acid secretion in the stomach decreases. As a result, the body is unable to break down food-based vitamin b12 into free form. Hence, the vitamin is not absorbed in the body which leads to deficiency.
Benefits of vitamin b12
The following are some significant health benefits of vitamin b12:
- Improves brain health:- Vitamin b12 is essential for proper functioning of brain and nervous system. Its deficiency can cause depression. Vitamin b12 also enhances memory and cognitive functions.
- Increases blood cells:- vitamin b12 is also necessary for the formation of red blood cells in the body. Its deficiency can cause anemia and also impair DNA synthesis. It also increases the white blood cells in the body that boosts immunity.
- Enhances skin and hair health:- Sufficient amount of vitamin b12 in the body improves skin and hair health. Its deficiency can cause skin conditions like vitiligo and hyper automation. Therefore, people suffering from eczema, psoriasis, inflammation, dryness and hair fall are recommended vitamin b12 supplements. It can also help treat dermatitis and acne.
- Reduces the risk of heart attack:- Vitamin b12 is also essential for reduction of homocysteine level in the body. Higher levels of homocysteine increases the chances of heart attack. Therefore, vitamin b12 improves heart health.
- Improves fertility:- Vitamin b12 also increases the functioning of the reproductive system in both men and women. It increases sperm count in men and decreases DNA damage in sperms. Studies suggest that many women suffering from infertility have vitamin b12 deficiency. Therefore, vitamin b 12 is essential for improving male and female fertility.
Daily requirement of vitamin b12
Our bodies store large amounts of vitamin b12. Therefore, you might not see vitamin b12 deficiency symptoms immediately. However, to prevent deficiency, you must take recommended amounts of vitamin b12 daily.
| Age | Recommended dosage (in mcg) |
| 0-6 months | 0.4 |
| 7-12 months | 0.5 |
| 1-3 years | 0.9 |
| 4-8 years | 1.2 |
| 9-13 years | 1.8 |
| 14-18 years | 2.4 |
| 18+ | 2.4 |
| Pregnant and breastfeeding women | 2.8 |
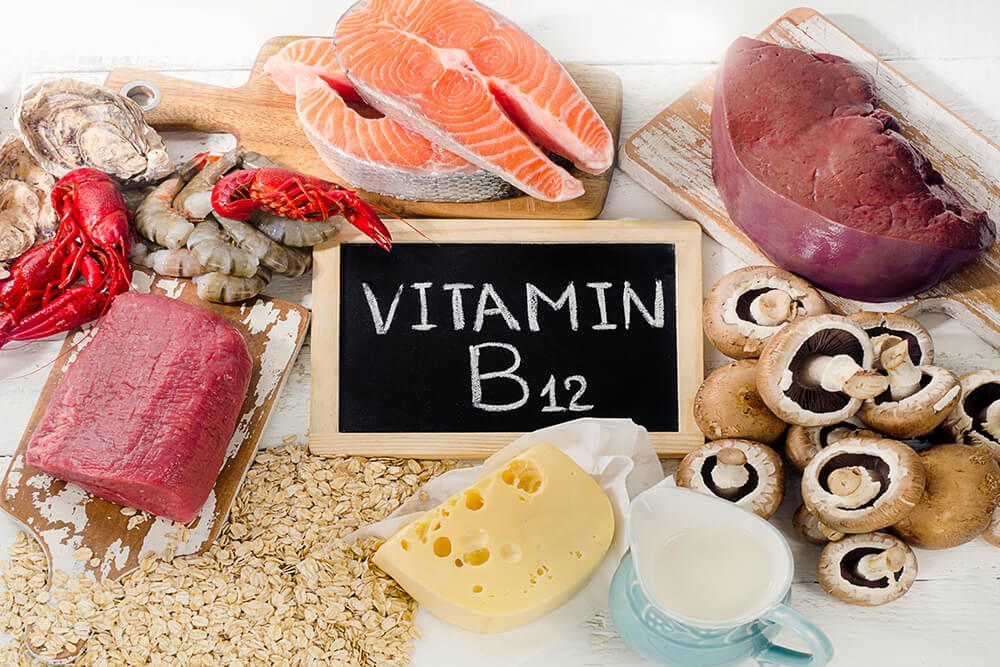
Vitamin b12 rich Food – Non Vegetarian
Animal foods are the best vitamin b12 sources. These are some food items with the highest amounts of vitamin b12.
- Fish:- Fish are one of the best b12 vitamin goods. Normal serving size of fish comprises 2.4μg vitamin B12 which meets the daily recommended dosage. Cooked clams have the highest amount of vitamin b12. One serving size comprises over 3500% of daily value. Oysters, tuna, crabs, and cooked trouts are also vitamin b12 rich foods. Even one serving of tuna and salmon have more than 300% of daily value of vitamin b12.
- Eggs:- One large hard-boiled egg comprises nearly 20% of daily recommended value of vitamin b12. Majority of the vitamin b12 in eggs is present in the yolk whereas egg white has small amounts of the vitamin. One cup of scrambled eggs has 70% of daily value. Goose eggs have the maximum amount of vitamin b12, over 300% of the daily value.
- Beef:- 100g of beef has 314% of daily value of vitamin b12. Beef hamburger and roast lamb have almost 100% of daily value.
- Chicken:- You can also have chicken for vitamin b12. 100 of chicken has 0.3 µg of vitamin b12.
Vitamin b12 rich food – Vegetarian
If you are looking for vitamin b12 sources for vegetarians, here are few health options for you.
- Dairy products:- Milk is one of the best vitamin b12 foods in India for vegetarians. 250 ml of milk consists of 1 mg vitamin b12. It is beneficial to meet the daily recommended dosage of milk. Cow milk comprises more vitamin b12 as compared to other animal’s milk. You can also have dairy products like yogurt and cheese.
- Nutritional yeast:- It is an activated form of yeast used to manufacture bread. You can also sprinkle nutritional yeast flakes on your food. Fortified nutritional yeast is a rich vitamin b12 source.
- Fortified cereals:- Rice, wheat, maize, oats, and other cereals are usually not vitamin b12 rich foods. However, these cereals are fortified. It means that vitamin b12 is added artificially to these cereals to provide you with recommended dosage of vitamin b12. Kellogg’s special K has 251% of daily value of b12.
Vitamin b12 food – Vegan
Vegan food options contain less amounts of vitamin b12. Here are some foods that you must include in your diet for vitamin b12.
- Soymilk:- 100g of unsweetened fortified soymilk has 51% daily value of vitamin b12.
- Tofu:- You can also have fortified tofu for vitamin b12. There is 137% of the daily value of b12 in one cup of fortified tofu.
Conclusion
Vitamin b12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is mainly found in animal foods. However, you can also have fortified vegetarian or vegan foods for daily value intake of vitamin b12. You can also have vitamin b12 supplements if you have vitamin b12 deficiency. However, before taking supplements, you must consult a doctor who will recommend a vitamin b12 test in Delhi to confirm deficiency.
FAQs
How to increase vitamin b12 naturally?
You can increase vitamin b12 naturally by having b12 vitamin foods like milk and milk products, beef, chicken and eggs. If you are a vegetarian, you can have fortified cereals, yogurt, and fortified nutritional yeast.
Are dry fruits rich in vitamin b12?
Nuts and seeds do not contain vitamin b12. It is best to include beef, fish and plenty of dairy products in your diet for vitamin b12.
Which is the best b12 vitamin food?
Clams, a type of fish, are the best vitamin b12 food. It has over 300% of daily recommended value of b12. Even eggs and beef have high amounts of vitamin b12.
References