What Is Ovulation: Meaning, Signs, Testing & Ovulatory Cycle
Overview of ovulation
Ovulation is the process that enables a woman to get pregnant. This process is when the eggs—stored in the ovary— are released in the fallopian tube for fertilization. The egg released is a mature egg and it can stay in the tube for 12 to 24 hours. Ovulation is a part of the menstrual cycle and occurs around the 14th day of the 28 days cycle. There might be times when ovulation does not occur at all.
Importance of ovulation
Ovulation plays a vital role in helping couples to plan for a baby. This is an important factor in helping the human species to keep the species alive while carrying the genetic line to another generation.
Apart from that, ovulation plays a vital role in regulating a woman’s health and overall well-being. In fact, women who have normal ovulation cycles are considered healthy, as the process of ovulation involves various hormones and glands. When ovulation occurs routinely, it indicates that the glands are functioning properly.
Symptoms of ovulation
Ovulation is a process that involves various hormones. This means that there will be certain symptoms that can help determine the window of ovulation. This is the time when a woman is most fertile. Knowing the symptoms of ovulation can help a woman to either conceive or avoid getting pregnant by taking accurate measurements.
The menstrual cycle differs from woman to woman. While some might have synced menstrual cycles, there is still a very little chance of having the same ovulation window, as the duration of the periods, along with other factors, like genetics or health effects, have to be taken into consideration. The common symptoms that indicate the onset of ovulation are:
-
- Changes will be seen in the cervical mucus. When the ovulation period nears, the body produces more estrogen, causing the mucus of the cervix to stretch and become clear. This helps the sperms to have a better path to reach the fallopian tube toward the matured egg.
- Vulval swelling is also seen. This is due to the increased levels of progesterone in the body that prepares the uterus for pregnancy and carrying of the fetus.
- Increased sex drive. When ovulation process starts, the sex drive in a woman increases, as it is one way the body is indicating that it is ready to conceive.
Signs that the body shows while experiencing ovulation
When a woman ovulates, there are various physical signs that can be easily observed and help women identify the window of ovulation. When the body undergoes hormonal changes, there are physical signs and discomforts. These are:
-
- Tenderness of the breasts
- Backaches and headaches
- Nausea
- Acne breakouts
- Spotting
- Increase in body temperature to sustain the mature egg
- Lower abdominal pains
- Extreme mood swings
- Increased senses, especially the sense of smell
This is also the time when pheromones are secreted, which help in attracting men.
Ovulation occurrence and tracking
There are millions of eggs in the ovaries, but only a couple of them get matured every month and are released to the fallopian tube. Keeping track of this occurrence is essential to ensure that pregnancy occurs. In order to understand and track ovulation, it is essential to be aware of the process that occurs before and after it and menstruation.
Following the lunar month of 28 days, the menstrual cycle consists of four stages where the body prepares itself to conceive a fetus. The failure of this starts the period. While the 28 days are considered average, the give and take for the cycle can be between 21 days to 35 days. This again depends on various factors. The four stages are:
Menses phase
Is when pregnancy does not occur and the uterine lining is shed via blood. This phase usually lasts for about 4 to 5 days. Once the menses phase is over, the body is prepared for another ovulation period.
Follicular phase
Is where the estrogen levels are elevated, which causes the uterine walls to thicken. The follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH also helps the follicles to grow and become mature. This phase lasts for about 14 days from the end of the menses phase.
Ovulation occurs
From the 14th day, when the luteinizing hormone helps with the release of the egg from the ovary.
Luteal phase
Lasts from the 15th day to the 28th day and during this phase, the mature egg reaches the fallopian tube, where it awaits fertilization. The uterus is prepared for pregnancy, as the progesterone hormone levels are elevated. If fertilization is successful, pregnancy occurs, or a drop in levels of both estrogen and progesterone causes the onset of the menses phase.
Ovulation & conception
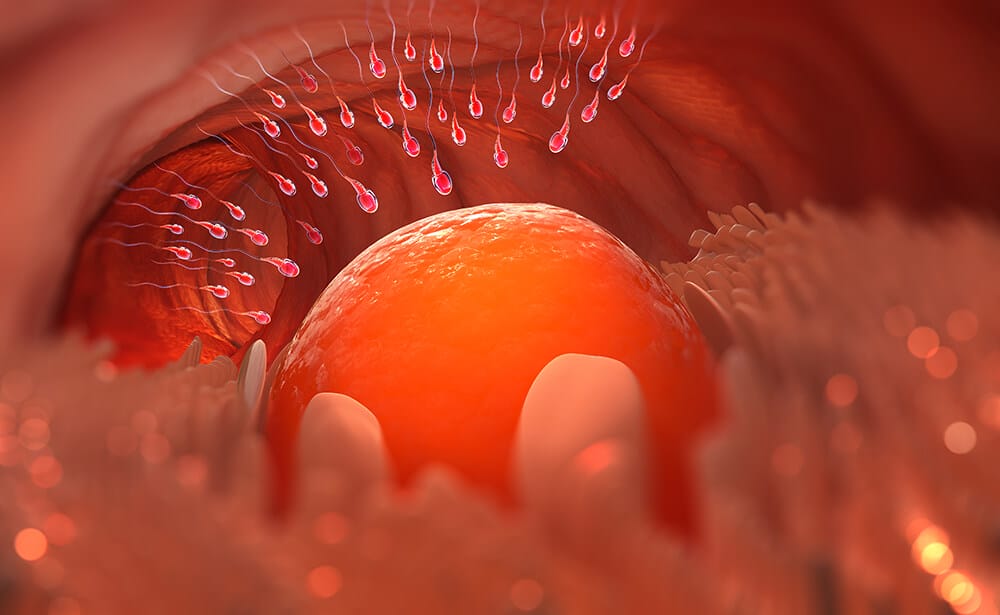
As mentioned above, ovulation occurs on the 14th day of a 28 days menstrual cycle. Or, it can be said that ovulation occurs in the mid-way of the menstrual cycle. A rise in the luteinizing hormone causes the mature egg to be released from the ovary. Then, this egg or ovum reaches the fallopian tube. When an ovulating woman has intercourse, the sperm enters the body, and upon reaching the fallopian tube, it attaches with the egg, resulting in fertilization.
The fertilization of the egg by the sperm causes the conception of the fetus. When sperm fertilizes the egg, the fertilized egg continues to move down the fallopian tube and divides into two cells. By the time the fertilized egg reaches the uterus, it becomes a cluster of cells, known as a blastocyst. This blastocyst then gets implanted into the walls of the uterus and then the process of pregnancy starts.
Testing for ovulation
Sperms can stay in the female body for about 4 to 5 days, whereas the mature egg stays in the fallopian tube for about 12 to 24 hours. This seems to be a really small window for conception, especially for women who are actively trying to get pregnant. If the ovulation time is not known, opting for ovulation testing is the best way to ensure conception.
Some of the best ways to test for ovulation are mentioned below:
Ovulation Predictor Test
Checks for a surge in the luteinizing hormone either through the urinary test or saliva test. The urine test at home is the most common test as it is more reliable. There is no fixed time to check the LH levels in the urine and it can be done any time of the day. The only thing to keep in mind is that the test should be done at the same time each day.
Basal Body Temperature Chart
Helps keep track of the basal body temperature and an increase in temperature around the estimated time of ovulation can indicate the release of the egg. When fertilization occurs, the temperature remains higher for a few days.
Progesterone level test
Can be done to check if the ovulation process is normal. When a woman has high progesterone levels during the 7th to 10th day of her cycle, it means that ovulation will occur normally.
Health conditions affecting ovulation
Lifestyle often affects the ovulation process, but there is no hard and fast rule that women who drink alcohol or smoke can never conceive. Some of the health concerns that adversely affect ovulation are:
Thyroid disorders
Having an overactive or underactive thyroid gland can affect ovulation. While certain symptoms might not always be very noticeable, some of them, such as lethargy, sudden change in weight, mood swings, etc are. Often people who show such changes are advised to get their thyroid tested.
Polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS
In this condition, the male hormone androgen is produced in higher levels in the women’s body. This causes hormonal imbalance, which can either delay ovulation or even completely stop the body from ovulating.
Hypothalamic dysfunction
This is a condition that is rare. When a woman works out excessively or has less than the required body fat, the hypothalamus functioning is disrupted. This leads to women not having their normal menstrual cycles, which further disrupts their ovulation.
Inducing ovulation
In some cases, ovulation has to be induced in order for the woman to get pregnant. This can be due to the woman not having the ovulation phase on her own, or even if she is ovulating normally, she is not getting pregnant. There are medications that are used in the ovulation induction process. These medications are:
-
- Clomiphene citrate
- Letrozole
- Thiazolidinedione
These medications stimulate the brain to think that the body is low on estrogen, causing the FSH to be released. Once FSH is released, the hormone works accordingly in maturing an ovum. Insulin-sensitizing agents are given to women suffering from PCOS.
Conclusion
Having a normal ovulation process is a sign of a healthy body. If the menstrual cycle and ovulation process are disrupted, consulting with a doctor becomes a must, for it can indicate other underlying disorders. Understanding the basics of ovulation is also the best way to avoid unwanted pregnancy.
FAQs
Do ovulation induction medications pose any risks?
There are reports that indicate that taking ovulation medications like aromatase inhibitors or AIs results in multiple pregnancies. But, apart from that, there are no serious conditions related to ovulation induction medications.
What is Hypothalamic amenorrhea?
Hypothalamic amenorrhea is the condition when the period stops due to the woman having lower than minimum body fat requirement. Excessive dieting and workouts can lead to this.
What is Hyperprolactinemia?
This is a condition that arises from the body producing a high amount of the hormone prolactin when pregnancy is not induced.